Industrial Laser Marking: A Comprehensive Guide for Manufacturers
Whether you’ve seen them at the checkout line, in a DVD player, or as a presentation pointer, lasers are an integral part of modern technology. However, not all lasers are the same. When it comes to manufacturing, industrial laser marking technology offers a highly sophisticated, permanent solution for tracking, labeling, and ensuring traceability in production lines.
Industrial laser marking technology has become a cornerstone for ensuring product identification, branding, and regulatory compliance across various industries. From automotive components to medical devices, laser marking offers a permanent, non-contact solution that outshines traditional methods in terms of durability and efficiency.
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the advantages of laser marking, the different types of systems available, and how manufacturers can choose the best solution for their specific needs. Whether you’re looking to enhance production efficiency or comply with industry regulations, industrial laser marking provides the flexibility and innovation required in modern manufacturing.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
Whether you’ve seen them at the checkout line, in a DVD player, or as a presentation pointer, lasers are an integral part of modern technology. However, not all lasers are the same. When it comes to manufacturing, industrial laser marking technology offers a highly sophisticated, permanent solution for tracking, labeling, and ensuring traceability in production lines.
Industrial laser marking technology has become a cornerstone for ensuring product identification, branding, and regulatory compliance across various industries. From automotive components to medical devices, laser marking offers a permanent, non-contact solution that outshines traditional methods in terms of durability and efficiency.
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the advantages of laser marking, the different types of systems available, and how manufacturers can choose the best solution for their specific needs. Whether you’re looking to enhance production efficiency or comply with industry regulations, industrial laser marking provides the flexibility and innovation required in modern manufacturing.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
In a Hurry? Take This Guide With
What Are Lasers?
Did you know the word laser is an acronym?
L.A.S.E.R. stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation, a technical term that describes the generation of a highly concentrated beam of light. The versatility of laser technology extends across various industrial applications, from marking and engraving to cutting and welding.
Lasers consist of:
- Gain medium: a material that works in tandem with electrical currents to stimulate the photons of light as they pass through
- Energy supply: Energy supply for lasers usually comes in electrical currents. These currents are “pumped” through the grain medium to stimulate the atom as light passes through. The pumping of electrical currents causes the light to bounce faster through the grain medium.
- A material to provide optical feedback: The materials chosen for optical feedback have one primary job: steering, or directing the beam of light through the gain medium to stimulate.
While the standard laser pointer used in conference rooms and lecture halls are safe for the user with no protection, part marking lasers fall into two classes governed by the CDRH — Class I and Class IV:
- Class I lasers are housed inside a safety enclosure. No laser radiation can escape from the enclosure, and the machine operator doesn’t need to take any additional safety precautions.
- Class IV means the laser is applied in an “open” configuration where the operator can be directly exposed to laser radiation. In this case, laser safety glasses are a must.
Both laser classes are used in industrial laser marking systems and can produce different results depending on the material being marked.
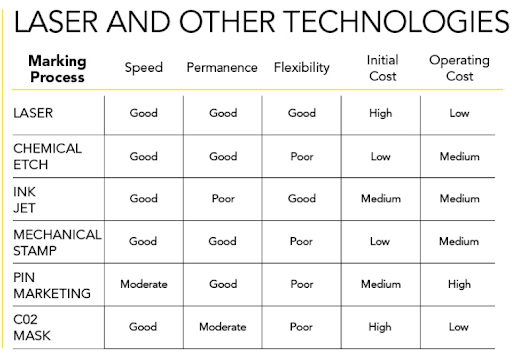
Advantages of Industrial Laser Marking Systems Compared to Other Methods
Laser marking is widely used across industries for its numerous advantages over other marking methods. The main benefits include:
- Permanency: Laser markings last as long as the part they’re etched onto.
- Non-contact: Lasers mark the surface without physical contact, reducing the risk of damage.
- Flexibility and versatility: Lasers can mark various materials, including metals, plastics, and elastomers.
- Low operating cost: Modern fiber-based lasers have no consumable parts, significantly reducing operating and maintenance costs.
- Innovation: The field of laser marking is continuously evolving, making systems more efficient and adaptable over time.
Laser marking equipment offers versatility, allowing users to mark different materials, such as metal, plastic, and rubber, without compromising the item’s integrity. The permanence of laser markings also deters counterfeiting, tracks production line efficiency, and enables accurate etching of barcodes and QR codes.
Laser marking has been adopted in numerous industries, including automotive, aerospace, military, defense, and medical applications. For instance, medical implants and tools can be marked without surface disruption to maintain smoothness. The precision and safety of laser marking make it an ideal solution in these highly regulated sectors.
Laser marking technology is versatile, cost-efficient, flexible, and safer than other options. Lasers require no tooling setup and little fixturing, greatly reducing the risk of surface damage.
Different Types of Industrial Laser Marking
Laser marking comes in various forms, each suited for different applications. The most common types are:
- General marking
- Annealing
- Ablating
- Deep engraving
- Plastic marking
1. General Marking
General marking is the most widely used due to its customizability and ease of programming. It can be adjusted to produce marks of varying intensity and colors, making it a versatile solution for marking steel, aluminum, and other materials. These marks are durable and suitable for long-term use.
2. Annealing
Annealing is a non-invasive form of laser marking that heats the material’s surface without causing physical disruptions. This method is important in medical applications where smooth surfaces are necessary, such as surgical tools or implants. Materials commonly used in laser annealing include stainless steel, chrome, cobalt, titanium, and elastomers.
3. Ablating
Ablating involves removing a surface coating to reveal the underlying material. Manufacturers use this technique on anodized aluminum, painted materials, and heat-treated surfaces to contrast the marked and unaffected areas. Ablating is especially useful for products that require highly visible, distinct marks.
4. Deep Engraving
Deep engraving uses a high-powered fiber laser marker to etch into materials like metal and rubber, creating a mark that goes beneath the surface. The depth of the engraving depends on variables such as power, speed, and frequency. By adjusting these factors, manufacturers can control the depth without compromising the item’s structural integrity.
5. Plastic Marking
Fiber lasers are especially effective for marking plastics due to their lower melting points than metals. In this process, lasers create a controlled “micro-burn” on the plastic’s surface, ensuring the part is marked without melting or damage.
The Role of Part Marking and Industrial Traceability
Part marking is essential for industries that must maintain high-quality control standards, track products, and ensure brand recognition. Industries such as medical devices, electronics, aerospace, and automotive have adopted laser marking for its precision, permanency, and ability to track parts throughout production.
A key application of laser marking is traceability. By marking a 2D barcode onto a part, manufacturers can track it through the entire assembly process. This visibility is crucial for:
- Configuration Management: Keeping track of which parts are used in specific assemblies.
- Production Bottlenecks: Identifying slow points in the assembly process to improve efficiency.
- LEAN Analysis: Monitoring the number of steps in the production process to optimize workflows.
Laser: Etching vs. Engraving
When considering industrial marking technologies, laser etching and industrial laser engraving are two commonly used methods that offer distinct advantages for manufacturers. While both involve using a laser to create permanent marks on various materials, the key difference lies in the depth of the mark and the method used to achieve it. Understanding these differences helps manufacturers select the best process for their specific applications.
Laser Etching
Laser etching is a process that alters the material’s surface by melting and expanding the material’s top layer. The beam raises the material’s surface slightly to create a high-contrast mark. Etching typically penetrates the surface to a depth of around 0.001 inches or less, making it a relatively shallow marking method compared to engraving. This process is ideal for creating detailed designs on materials like metals, plastics, and ceramics. Etched marks are durable and resist wear, making them suitable for applications where surface-level identification is needed, such as barcodes or serial numbers.
One advantage of laser etching is its speed. Because it only affects the surface layer, it’s faster than deeper marking methods, making it more efficient for high production. Laser etching is versatile, as it can be used on several materials, including coated or anodized metals. However, since it doesn’t remove much material, etched marks may be less resistant to extreme environmental conditions than engraved marks.
Laser Engraving
On the other hand, an industrial laser engraving machine removes material to create deeper marks. The laser vaporizes the surface layer, producing an indentation ranging in depth from 0.002 to 0.005 inches, and sometimes even deeper, depending on the material and application. Because of its depth, a commercial laser engraving machine produces highly durable marks that withstand harsh conditions, including abrasion, heat, and chemical exposure.
Industrial laser engraving is commonly used for part identification, branding, or traceability in various industries, like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where long-lasting, tamper-resistant marks are essential. This method is particularly well-suited for metals but can also be used on plastics, wood, and other materials. Although engraving takes more time than etching due to the removal of material, it ensures a mark that is resistant to wear and difficult to remove.
Choosing Between Laser Etching and Engraving
The choice between laser etching and engraving depends on several factors, including the material being marked, the required mark depth, and the environment in which the marked part will be used. A laser etching machine may be the best option if a high-contrast, surface-level mark is sufficient and speed is a priority, However, if durability is a key concern and the mark needs to withstand extreme conditions, laser engraving is the more appropriate choice.
Laser Marking Source | Laser Types & Selection Considerations
Laser marking technology offers manufacturers several different source types, each with benefits and best-use applications. The main types of laser marking sources are fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, green lasers, and UV lasers. Selecting the right laser source depends on several factors, including the material being marked, the required mark depth, and the precision necessary for the application.
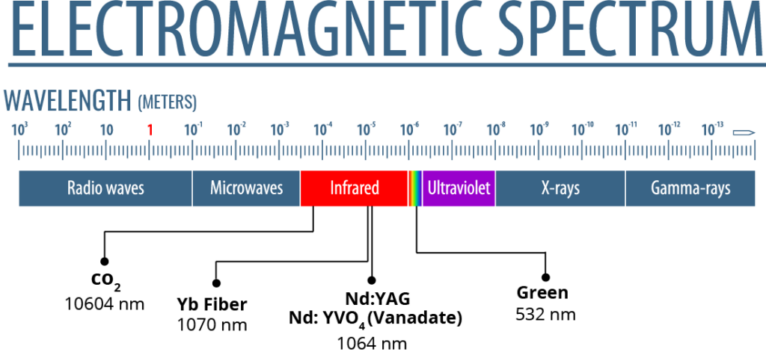
Different sources include:
Fiber Lasers
Fiber laser marking machines are widely used for marking metals and plastics, providing high power and efficiency. They amplify light through optical fibers, making them ideal for marking hard materials like steel, aluminum, and brass. These lasers are known for their durability and low maintenance costs. They also produce high-quality, permanent marks that are resistant to wear, making them popular in automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
CO2 Lasers
CO2 lasers, which use carbon dioxide gas to generate the laser beam, are well-suited for non-metallic materials such as wood, leather, glass, and certain plastics. These lasers operate at longer wavelengths than fiber lasers, which makes them effective for engraving or cutting organic and non-metal materials. CO2 lasers are a go-to solution for marking items such as packaging, textiles, and signage, offering speed and flexibility.
Green Lasers
Green lasers, which operate in the visible light spectrum, mark reflective materials like copper, gold, and silver. They are also effective on plastics and ceramics, providing high-contrast marks without damaging the substrate. Their shorter wavelengths enable precise marking, especially on sensitive materials, making them a preferred choice for industries that require precision, such as medical device manufacturing and electronics.
YAG Laser
Like the fiber laser, the YAG laser emits light at a wavelength of 1.064 micrometers. However, its internal structure differs, with the beam passing through distinct crystals to generate the laser output.
The YAG laser is well-suited for marking metals and plastics in its standard configuration. However, it can also be used to mark more delicate materials with appropriate adjustments.
UV Lasers
UV lasers operate at a very short wavelength, allowing for cold marking, where the material is marked without generating heat. This is particularly useful for sensitive materials that other lasers might damage. UV lasers are excellent for marking glass, plastics, and semiconductors. Their ability to produce micro marks makes them a favorite in industries requiring detailed and delicate engraving, such as pharmaceuticals and electronics.
Choosing the Right Material for Industrial Laser Marking Machines
Different materials respond differently to laser marking, making material selection an essential consideration in optimizing laser marking systems. The type of material determines the laser wavelength that should be used and affects the final mark quality, contrast, and durability.
Different materials include:
Metal
Metals like steel, aluminum, and brass are widely used in laser marking due to their excellent absorption of laser energy, especially with fiber lasers. Fiber lasers are highly efficient at marking metals because they operate at a wavelength allowing for deep and permanent marks. Laser engraving is commonly used for metal parts requiring durable identification, branding, or part traceability. On the other hand, laser etching is suitable when a faster process or surface-level marking is needed.
Plastics
Plastics, including ABS, polycarbonate, and acrylic, are frequently marked using CO2 or fiber lasers. The specific laser type and wavelength needed for marking plastic depend on its chemical composition. Laser marking plastic often involves creating high-contrast marks without damaging the part’s integrity. A lower-power laser may be used to avoid distorting the plastic material, while still achieving legible marks. Laser marking is commonly used in electronics, packaging, and medical devices, where plastic is prevalent.
Ceramics and Glass
Ceramics and glass present unique challenges for laser marking. CO2 lasers are often best for marking these materials due to their longer wavelengths, which efficiently mark non-metallic surfaces. For more delicate applications, such as pharmaceuticals or electronics, UV lasers may be used for cold marking to prevent material damage. UV lasers create exact marks without generating heat, making them suitable for sensitive materials like glass.
Wood and Organic Materials
CO2 lasers excel at marking organic materials, including wood, leather, and textiles. The longer wavelength effectively burns or etches the surface of these materials to create marks. The type of laser marking system chosen for wood and organic materials depends on the desired depth and speed of marking. CO2 lasers are commonly used in the signage and furniture industries, where engraving or etching provides a clean and precise finish.
Tips for Selecting the Best Laser Marking System
Once the material is selected, choosing the right laser marking system involves several considerations to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Understand Your Marking Needs
The first step in choosing the best laser marking system is to define your needs. Do you require deep engraving, surface etching, or high-contrast marking? Durability and traceability are critical in manufacturing, so a system that can perform deep laser engraving might be the best choice. For industries like electronics, where legibility is key, high-contrast etching may be more suitable.
Match the Laser Wavelength to the Material
Matching the laser’s wavelength to the material ensures efficient marking. For instance, fiber lasers are highly effective for marking metals, while CO2 lasers are better suited for non-metallic materials. UV lasers offer a solution for marking delicate or heat-sensitive materials like glass and certain plastics. By aligning the wavelength with the material, manufacturers can avoid issues like poor mark quality, slow processing times, or damage to the material.
Consider the Marking Environment
The operating environment also plays a role in selecting the best laser marking system. Harsh environments, such as those in heavy manufacturing or outdoor settings, may require a rugged system that can withstand dust, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress. For example: Controlled environments like electronics assembly or medical device manufacturing require precision and cleanliness. A system with fine-tuned settings and a clean marking process, such as UV or green lasers, would be more appropriate.
Evaluate Speed and Efficiency
Production efficiency is another critical factor when choosing a laser marking system. High-speed marking systems may be required for mass production applications, such as automotive or electronic parts, where thousands of components must be marked quickly and consistently. In contrast, industries requiring detailed customization, like jewelry or medical devices, may prioritize accuracy over speed, making a slower but more precise system preferable.
Choose a Versatile System
A versatile laser marking system is valuable for businesses working with multiple materials or requiring different types of marks. Many manufacturers opt for systems that accommodate different materials and can switch between marking modes, such as engraving and etching. This flexibility allows for greater adaptability and future-proofing, as business needs evolve.
Maintenance and Support
Consider the long-term operation and support of the laser marking system. Regular maintenance and access to technical support are essential to keeping the system running efficiently. Many modern laser systems are designed with durability in mind, requiring minimal upkeep, but understanding the level of manufacturer support and available warranties can help prevent costly downtime.
Industrial Laser Marking vs. Dot Peen Marking: Best Use Cases
Laser and dot peen markings offer durable, permanent marks, but differ in their marking process, speed, and versatility. Each technology has specific applications where it excels, making the choice between them highly dependent on the industry and materials involved.
Laser Marking
Laser marking uses a concentrated beam of light to etch or engrave the surface of a material. It offers precision and versatility, making it ideal for industries that require high-quality, permanent marks without damaging the material. Laser marking is often used for branding, traceability, and compliance purposes in the following industries:
- Automotive: The automotive industry relies on laser marking for part identification and traceability, particularly metal parts like engine components, transmissions, and brake systems. The high precision and durability of laser marking ensure that part numbers and serial codes remain readable over time, even in harsh environments.
- Medical Devices: Laser marking creates high-contrast, sterile marks on surgical instruments, implants, and medical devices. There is no contact with the part, ensuring no contamination risk. The marks remain clear and legible, even after repeated sterilization.
- Electronics: For industries like electronics and semiconductors, where space is limited, laser marking excels in creating precise, tiny marks that can include barcodes, QR codes, and alphanumeric characters. The ability to mark delicate surfaces without causing damage is a major benefit.
Dot Peen Marking
Dot peen marking, also known as pin marking, uses a mechanical pin to indent the surface of a material, creating a series of dots that form a readable mark. This process is particularly well-suited for rugged environments and applications that require deep, permanent marks. Dot peen marking is commonly used in the following industries:
- Heavy equipment and manufacturing: Dot peen marking is ideal for heavy equipment and manufacturing sectors, including aerospace, defense, and oil and gas. It can create deep, durable marks that withstand harsh conditions, such as exposure to high temperatures, chemicals, and mechanical wear.
- Metalworking: For industries dealing with hardened metals, dot peen marking provides the depth and permanence needed to identify large parts or components. It’s often used in metal fabrication for marking tools, dies, and steel components.
- Construction: In industries such as construction, where parts may be exposed to outdoor elements and heavy use, dot peen marking offers a rugged solution for part identification. The deep marks created by dot peen machines ensure that information remains legible over time, even when exposed to harsh weather conditions.
Choosing the Right Marking System for Industrial Applications
Selecting the appropriate marking system for an industrial facility involves several key factors, including the types of materials being marked, the production environment, and the required mark characteristics. Below are some important considerations to help guide the decision-making process.
Material Compatibility
Different marking systems are better suited to certain materials. As mentioned, laser marking excels in industries where precision and non-contact marking are critical, particularly for metals, plastics, ceramics, and delicate materials. Dot peen marking, on the other hand, is ideal for metals and hard materials where deep, rugged marks are necessary.
Understanding your material’s properties and how it reacts to different marking technologies will help you select the best system. For example, fiber lasers are optimal for marking metals, while CO2 lasers are more effective on non-metallic materials like glass or plastic.
Production Speed and Volume
Production speed is a significant factor when choosing between laser and dot peen marking systems. Laser marking is generally faster and more efficient for high-volume production runs, making it a popular choice for industries that require rapid throughput, such as automotive manufacturing or electronics assembly.
Dot peen marking is slower due to the mechanical nature of the process, but it offers deeper, more durable marks. This makes it suitable for low- to medium-volume applications where durability is prioritized over speed, such as aerospace or construction sectors.
Environmental Factors
The environment in which the marking system will be used is critical. In industries where dust, debris, or temperature extremes are common, the robustness of dot peen marking may be more suitable. Laser marking systems are often used in clean environments like medical device manufacturing, where precision and cleanliness are paramount.
Type of Mark
The type of mark required can also dictate the best system for your needs. Laser marking is ideal for high-resolution, detailed marks such as logos, barcodes, and intricate patterns. In contrast, dot peen marking creates deeper, more tactile marks for applications requiring long-lasting identification under harsh conditions, such as steel beams or industrial components.
System Maintenance and Durability
Maintenance requirements and system longevity should also factor into your decision. Dot peen machines typically require more maintenance due to the mechanical components, such as the marking pin, which can wear down over time. Laser marking systems are non-contact and free of consumable parts. This means they generally have lower maintenance needs, though they may require occasional recalibration to maintain precision.
10 Industrial Part Marking Considerations
Several factors must be considered to ensure the industrial part marking method aligns with the specific application needs. From material type to regulatory compliance, making informed decisions about marking systems is crucial for maintaining traceability, branding, and overall product quality. Here are 10 key considerations to keep in mind when selecting an industrial part marking system:
1. Material Type
Different materials react differently to marking methods. Metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites each require tailored marking approaches. For instance, fiber lasers work well with metals, while CO2 lasers are more effective on non-metallic materials like plastics or glass.
2. Marking Depth
The required marking depth depends on the application. Laser etching, for example, creates surface-level marks suitable for many identification needs, whereas laser engraving or dot peen marking offers deeper, more durable marks for heavy-duty applications.
3. Contrast and Visibility
Marks need to be easily readable, especially for traceability or compliance purposes. High-contrast marks ensure that barcodes, serial numbers, or logos remain visible even after exposure to wear or harsh environments.
4. Durability
Marks must withstand extreme conditions In industries like aerospace, automotive, and defense, including abrasion, chemicals, and high temperatures. Laser engraving and dot peen marking provide the durability necessary for these demanding environments.
5. Marking Speed
For high-volume production, the speed of the marking process is critical. Laser marking systems are typically faster than mechanical systems like dot peen marking, making them ideal for industries requiring rapid throughput.
6. Precision
Applications like electronics and medical devices require precision and detail in the markings. Laser marking provides high accuracy for marking small components with intricate designs, barcodes, or identification numbers.
7. Compliance and Traceability
Many industries are subject to strict regulations for traceability, requiring permanent and readable marks for product identification. The marking system must meet industry standards for compliance and traceability, especially in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
8. Environmental Conditions
Consider the operational environment. If parts will be exposed to harsh conditions, such as high humidity, extreme temperatures, or mechanical wear, opt for marking methods like dot peen or deep laser engraving, which offer superior resilience.
9. Type of Mark
The type of mark, whether it’s a logo, serial number, or barcode, can impact the marking process. Laser marking is well-suited for high-resolution marks, while dot peen excels at creating durable, deep marks for part identification.
10. Cost and Maintenance
Finally, assess the marking system’s cost and maintenance requirements. While laser systems may have higher initial costs, they often require less maintenance and offer a longer lifespan than mechanical systems like dot peen machines.
By carefully considering these factors, manufacturers can select the most appropriate industrial part marking system, ensuring efficiency, durability, and compliance across their production processes.
Technomark: Leading the Way in Industrial Laser Marking Solutions
Technomark provides advanced permanent marking solutions using laser technology, specifically designed with ergonomic features and compact sizing to seamlessly integrate into production lines, warehouses, or workshops. All of Technomark’s laser devices utilize fiber technology, enabling fast, precise marking on a variety of materials. Renowned for their high-speed capabilities, these solutions are ideal for deep or light engraving, decorative applications, and part identification, ensuring comprehensive traceability across any component.
Adaptive Laser Marking Station
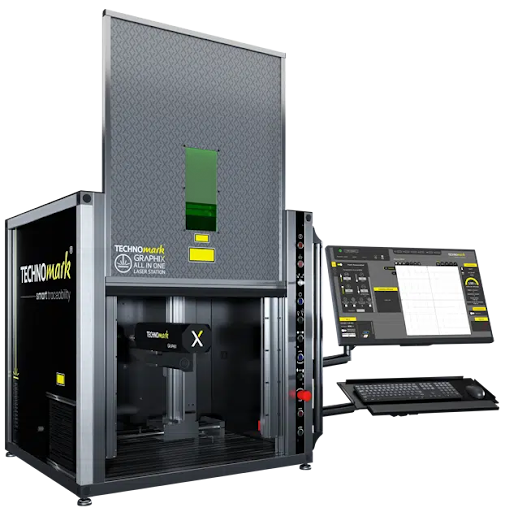

The Technomark Graphix Plus system is a versatile and powerful solution for industrial marking, offering a unique combination of performance, precision, and ease of use. Designed for marking small to medium-sized parts, the Graphix Plus system integrates both the marking head and electronics into a single, all-in-one station. This streamlined setup simplifies installation and operation, making it an ideal choice for facilities looking to enhance their marking capabilities without compromising on space or functionality.
One of the standout features of the Graphix Plus is its ergonomic design, highlighted by an automated electrical door that opens up to 580 mm, allowing easy access to parts for quick loading and unloading. The station is equipped with a motorized X-axis, enabling horizontal movement of the marking head, which can cover an extended marking area of up to 475 mm. This functionality, combined with programmable software-controlled settings, supports efficient marking for both single pieces and small production series.
The system’s marking capabilities are highly adaptable, with support for a variety of marking types including alphanumeric characters, 2D Datamatrix, logos, timestamps, and barcodes. Additionally, the Graphix Plus system offers multi-level marking, making it possible to mark on parts with varying heights or complex geometries, such as stepped or curved surfaces. This precision is achieved through Technomark’s proprietary multiplane software function, which optimizes the laser path in three dimensions.
To further enhance usability, the Graphix Plus features an intuitive software interface with two operating modes—Creation and Production. Creation Mode is tailored for novice users, offering simplified settings to facilitate easy file creation, while Production Mode provides pre-configured files for repetitive tasks, reducing the risk of errors and maximizing productivity. This flexibility ensures that both new and experienced operators can effectively use the system.
Technomark also prioritizes customer support, offering a range of pre-sale and after-sales services such as feasibility studies, training, equipment loan, and repair services. With a strong global presence in 47 countries and more than 22,500 machines in operation worldwide, Technomark continues to deliver high-quality marking solutions across diverse industries.
Technical Highlights
- Power ratings: 20W or 30W
- Focal lengths: 254 mm for a 140 x 140 mm window and 160 mm for a 100 x 100 mm window
- Multiple marking types: Alphanumeric, 2D Datamatrix, logotype, timestamp, barcode
- Compatible with various materials, supported by an integrated materials database
- Optional accessories: D-axis for cylindrical part marking, fume extractor
The Technomark Graphix Plus system is designed to streamline marking operations, offering robust features and flexible configurations to meet the demands of modern manufacturing environments. Whether for high-precision markings or more general applications, the Graphix Plus provides a reliable solution that combines advanced technology with ease of use, ensuring high-quality results with every mark.
Industrial Marking Solutions
Technomark offers the Graphix Inline Laser Marking Machine for larger-scale automated production. The Technomark E-Series laser marking system is a robust and adaptable solution designed to meet the diverse needs of industries requiring high-quality, permanent markings on various materials. This system stands out for its modular design, which allows it to be used as either a workstation for manual loading and marking or integrated into a production line for automated, continuous marking processes. The versatility of the E-Series ensures that it can be customized to fit a wide range of industrial applications, from small-scale projects to high-volume production environments.
https://www.technomark-inc.com/contact-us/The E-Series laser marking system is built around fiber laser technology, known for its precision and durability. This technology provides a concentrated, high-intensity beam that can mark metals, plastics, and other substrates with exceptional accuracy. It is capable of performing both deep and surface-level markings, making it a versatile tool for industries like aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and more. The system’s precision ensures legibility and longevity, even for the most complex markings such as 2D Datamatrix codes, barcodes, and alphanumeric characters.
One of the key benefits of the E-Series is its ease of integration. The system can be seamlessly incorporated into automated production lines, thanks to its compact design and flexibility in mounting configurations. Additionally, it features a robust software interface that allows for easy creation, modification, and execution of marking files. The software supports variable data inputs, making it suitable for serial numbers, batch codes, or other dynamic data that may change from part to part.
In terms of usability, the E-Series offers a user-friendly interface with a variety of features designed to streamline the marking process. The system includes a Smart View function, enabling operators to visually align parts before marking, which reduces errors and increases efficiency. The laser path can also be optimized through Technomark’s multi-plane software, which accounts for multi-level surfaces or parts with varying heights. This makes the E-Series particularly effective for marking on irregularly shaped or stepped surfaces.
Key Features of the E-Series
- Modular design: Can be used as a standalone workstation or integrated into production lines
- Fibre laser technology: Provides deep and precise marking on metals, plastics, and other materials
- Smart View function: Visual alignment before marking to improve accuracy
- Multi-plane software: Optimizes marking on parts with complex geometries
- User-friendly interface: Easy file creation, variable data input, and file management
- Compact design: Allows for easy integration into existing workflows
With its powerful fiber laser technology and versatile modular design, the Technomark E-Series is a top choice for industries that require reliable, high-quality marking solutions. Whether used as a standalone system or integrated into a larger production line, the E-Series provides consistent, precise results, making it an essential tool for any company focused on quality and efficiency in their marking processes.
Industrial Laser Marking: Standing the Test of Time
Industrial laser marking stands out as a transformative technology, offering unparalleled advantages over traditional marking methods. From ensuring traceability and compliance to enhancing brand integrity and combating counterfeiting, laser marking empowers manufacturers across diverse industries to achieve excellence in their production processes.
The versatility of laser marking — from etching and engraving to annealing and ablating — ensures that every unique material and application requirement is met with precision and reliability. Whether you’re operating in the automotive, medical, electronics, or aerospace sector, the right laser marking system can significantly boost your operational efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and provide marks that stand the test of time.
Take the Next Step with Technomark
Ready to elevate your manufacturing processes with cutting-edge laser marking solutions? Technomark is at the forefront of industrial laser technology, offering tailored systems that meet your specific needs — whether you’re handling low-volume, high-matrix jobs or managing large-scale automated production. Our expert team is dedicated to helping you choose and implement the perfect laser marking system to enhance your productivity and ensure lasting quality.
Don’t let outdated marking methods hold you back. Contact Technomark today to discover how our innovative laser marking solutions can transform your manufacturing operations. Visit our website or reach out to our specialists to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a more efficient, precise, and reliable production future.




