Data Matrix vs QR Codes: Choosing the Right Code For Your Needs
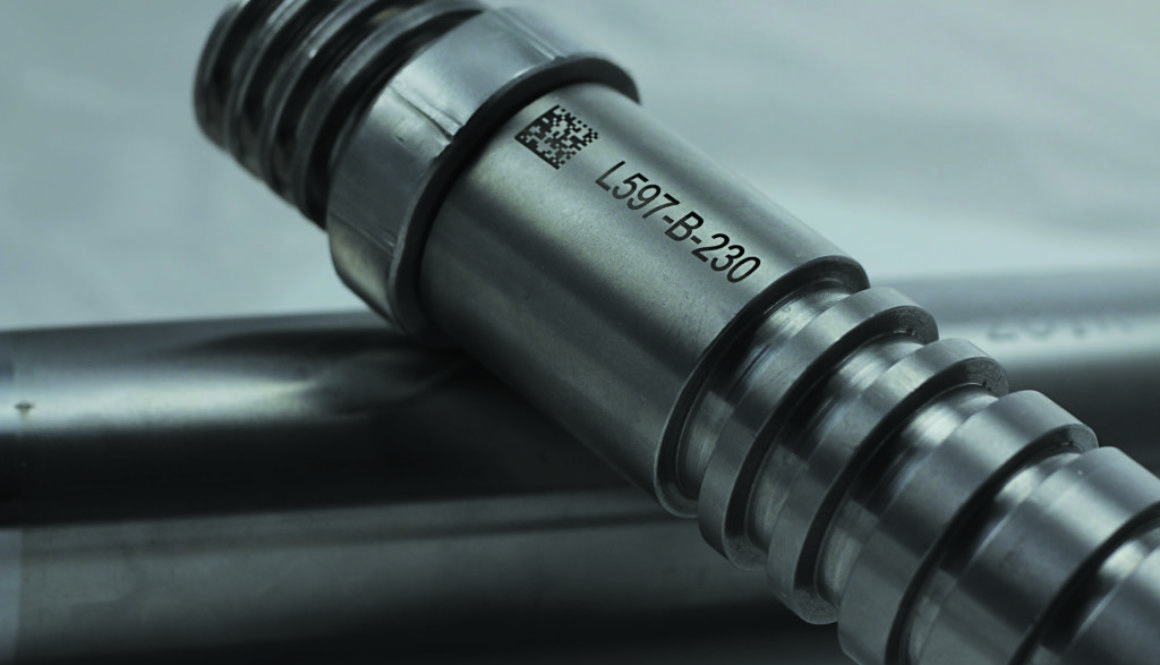
Have you ever wondered about the small, square barcodes often found on electronic devices, tools, and appliances? While they might resemble QR codes, they’re actually Data Matrix codes, essential components of modern manufacturing processes.
Unlike QR codes, primarily used for consumer-facing applications like websites and social media, Data Matrix codes are designed for efficient data storage and traceability. They’re the only 2D barcodes officially approved by GS1 for regulated healthcare items, emphasizing their reliability and accuracy.
QR codes on the other hand are larger and contain more data, such as website URLs, and can encode information in numeric and alphanumeric form as well as Kanji and other multi-byte character sets.
No matter what industry, when it comes to industrial traceability for manufacturers, choosing the right type of code can leave a production run riddled with misinformation and the chance of getting lost.
Let’s break down the differences and similarities between QR and Data Matrix codes and why the latter is the preferred choice of most manufacturers.
QR vs Data Matrix Codes
Understanding the distinctions between QR codes and Data Matrix codes is crucial for manufacturers looking to optimize their processes. Both codes are two-dimensional (2D) barcodes and consist of a pattern of squares that can be read by a barcode scanner. However, there are notable differences in their shape, size, and data capacity.
What is a QR Code?

QR codes are two-dimensional barcodes scanned by smartphones or other devices with cameras. They store information in a matrix of black-and-white squares, which can be interpreted to reveal data such as URLs, text, or contact information. Think of them as digital links that can be quickly accessed by simply scanning them with your phone.
What is a Data Matrix Code?
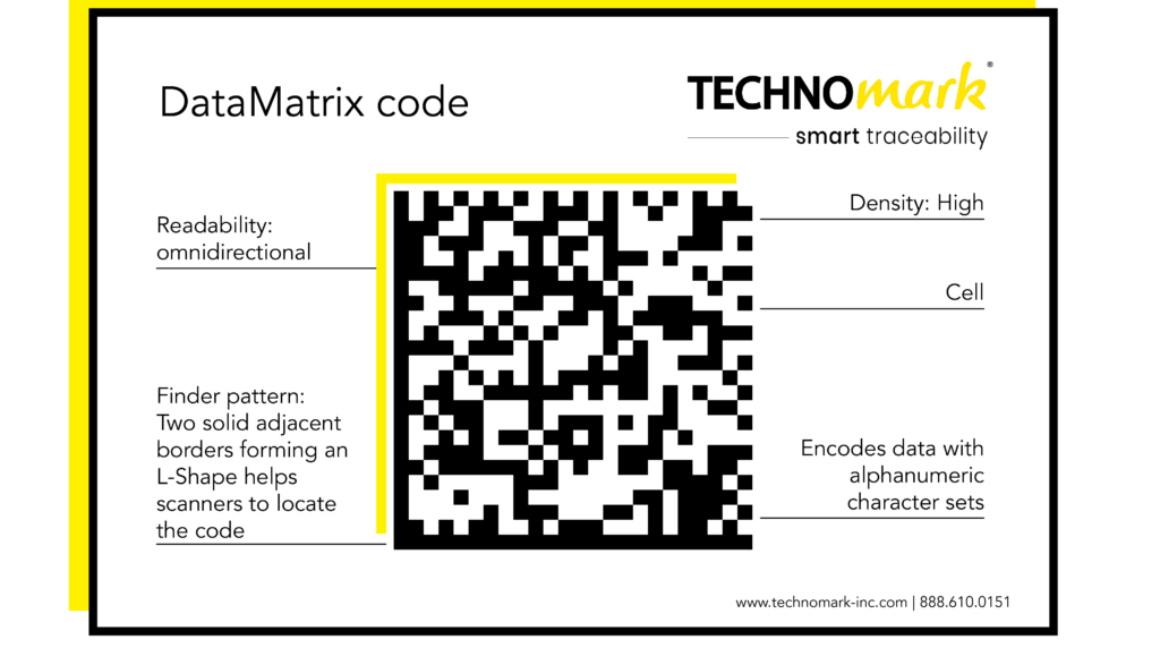
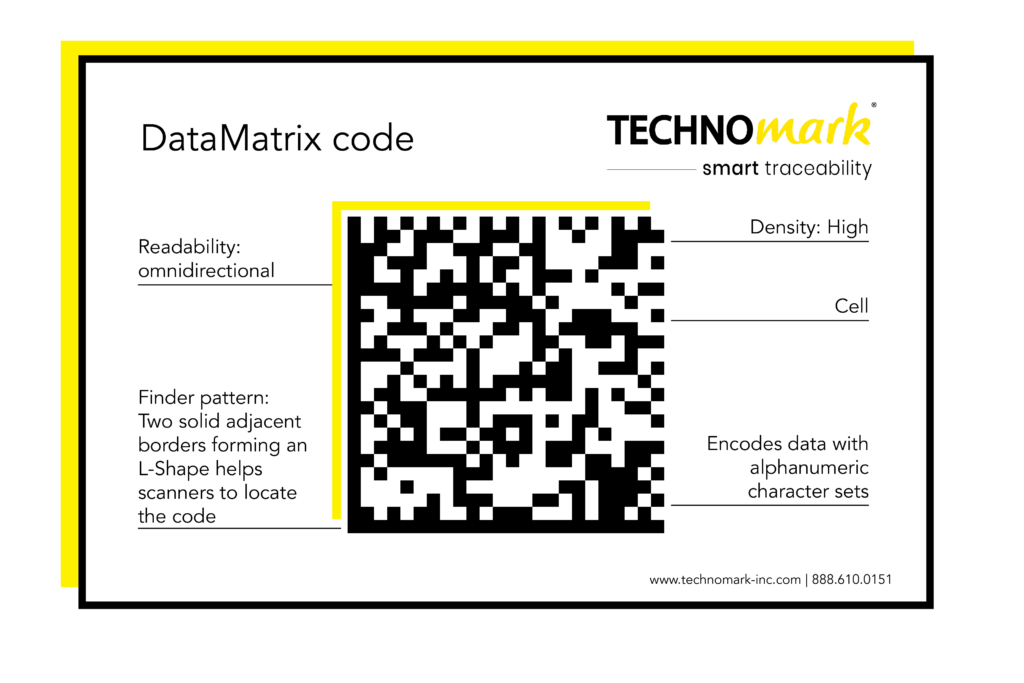
 Data Matrix codes are another type of two-dimensional barcode, but they are smaller and more compact than QR codes. They are often used in industrial settings, such as manufacturing and logistics, because they are highly durable and can be scanned even when damaged or dirty. Data Matrix codes are useful for tracking individual items or components throughout production, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
Data Matrix codes are another type of two-dimensional barcode, but they are smaller and more compact than QR codes. They are often used in industrial settings, such as manufacturing and logistics, because they are highly durable and can be scanned even when damaged or dirty. Data Matrix codes are useful for tracking individual items or components throughout production, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
Direct Part Marking
While both QR and Data Matrix codes are in the public domain and can be used royalty free, Data Matrix codes have become the standard for anti-counterfeit measures, part identification, and internal tracking because they feature advanced error-correcting techniques that are more robust than QR codes.
This presents a unique benefit for manufacturers that need to ensure their products can be identified if part of the mark gets damaged or impeded.
Particularly necessary for complex and high stakes industries such as medical, aerospace, and defense, where hundreds to thousands of components are needed in order to assemble a finished product, Data Matrix codes can be read even if up to 50% of the mark gets damaged.
QR codes on the other hand have steadily been adopted in consumer-facing applications. These codes can be found everywhere from business cards to product packaging, containing links to websites, resumes, premium offers, and even restaurant menus.
QR codes have a lower level error-correcting built in, and can be rendered useless with even slight ware and tare. Just 30% of a QR code needs to be damaged before it becomes unreadable.
While these codes are perfect for consumer-forward use, marking a component or part with a QR code presents a real danger for misidentification pending the mark gets damaged.
Data Matrix vs QR Codes | Uses Cases and Applications
| Data Matrix |
|---|
| Supply chain traceability |
| Anti-counterfeiting through serialization |
| Part identification |
| QR code |
|---|
| Additional product information |
| Usage instructions |
| Social sharing |
| Auto-linking for spare ordering and registration |
| Promotions, contests, and gamification |
Specifications of Data Matrix vs QR Codes
While Data Matrix codes are typically reserved for industrial use cases, both types of marks can play a role in the manufacturing industry.
Since both DataMatrix and QR codes are GS1 approved, they can carry any GS1 ID keys including:
| Used to Identify |
|---|
| Products and services |
| Parties and locations |
| Returnable assets |
| Assets |
| Service provider and recipient relationships |
| Components and parts |
| Product model |
| Example |
|---|
| Can of soup, chocolate bar, music album |
| Companies, warehouses, factories, stores |
| Pallet cases, crates, totes |
| Medical, manufacturing, transport and IT equipment |
| Loyalty scheme members, doctors at a hospital, library members |
| Automobile parts |
| Medical device |
Beyond GS1, specifications and requirements for each code are presented by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). For more about how these codes work themselves, and how to create them, you can check out the relevant ISO standard for more detail.
Requirements for Data Matrix codes are specified under the ISO/IEC 16022 international standard; while requirements for QR codes are specified under the ISO/IEC 18004 international standard.
Best Practices for Implementing Data Matrix Codes in a Manufacturing Process
Implementing Data Matrix codes in a manufacturing process can significantly enhance traceability, efficiency, and accuracy. However, to fully leverage the advantages of this technology, it’s crucial to follow best practices tailored to the specific needs of your operations.
Best practices for implementing Data Matrix codes include:
- Ensuring that the code is applied in a location on the part that is less likely to be damaged or exposed to harsh conditions.
- Using direct part marking methods like laser marking or dot peen to create a durable, permanent code that can withstand wear.
- Regularly testing and verifying the readability of the code throughout the production process.
- Incorporating advanced scanning equipment that can easily read Data Matrix codes, even when partially obscured or damaged.
- Consulting with an industrial marking expert to ensure the correct code placement, size, and method of application for long-term durability.
Frequently Asked Questions About Data Matrix and QR Codes:
How Do the Error-Correcting Capabilities of Data Matrix Codes Compare to QR Codes in Practical Applications?
Data Matrix codes have more robust error-correcting features compared to QR codes. They can still be accurately read even when up to 50% of the code is damaged, making them more reliable in harsh environments like manufacturing or logistics. QR codes, on the other hand, lose readability once about 30% of the code is damaged, making them more prone to failure in industrial settings where wear and tear are common.
Are There Significant Cost Differences Between Implementing QR Code & Data Matrix Code Systems?
The cost of implementing QR or Data Matrix codes can vary depending on factors such as the specific hardware and software used, the complexity of the system, and the volume of codes needed. In general, Data Matrix codes may be slightly more expensive to implement due to the specialized equipment required for their reading and writing. However, the long-term benefits of using Data Matrix codes, such as improved traceability and efficiency, can often outweigh the initial costs.
Are There Differences in Scanning Speed & Accuracy Between QR & Data Matrix Codes, Especially When Used in High-Speed Industrial Settings?
While both QR and Data Matrix codes can be scanned at high speeds, Data Matrix codes often have a slight advantage in terms of scanning accuracy. Their smaller size and denser data encoding make them less prone to misreading, especially in challenging conditions.
Direct Part Marking | Best Practices and Proven Methods
Understanding the differences between QR codes and Data Matrix codes, and choosing which is best for your application can get overwhelming. That’s why its important to consult a trusted advisor and partner.
Technomark has been operating and supplying expertise with industrial marking equipment since 2000. Since 2018, Technomark North America has been the only established OEM of dot peen and laser marking systems — the primary methods for direct part marking — with a headquarters in the USA.
Technomark has been at the forefront of industrial marking innovation, developing machines for seamless integration in manufacturing processes.
Our goal is to help our customers:
- Increase machine uptime
- Decrease total cost of ownership
- Make part marking and identification simple and cost-effective
- Bring new ideas to the table to increase efficiency
Your relationship with Technomark North America shouldn’t be limited to a strict supplier-to-customer interaction. We value communication above all else, which is why our team is dedicated to finding ways to solve your traceability challenges through a consultative process.
Interested in learning more about Direct Part Marking using Laser Technology? Check out our free ebook below: